STM32保存BMP图片
此例程需要FATFS来配合使用
//BMP编码函数
//将当前LCD屏幕的指定区域截图,存为16位格式的BMP文件 RGB565格式.
//保存为rgb565则需要掩码,需要利用原来的调色板位置增加掩码.这里我们已经增加了掩码.
//保存为rgb555格式则需要颜色转换,耗时间比较久,所以保存为565是最快速的办法.
//filename:存放路径
//x,y:在屏幕上的起始坐标
//mode:模式.0,仅仅创建新文件的方式编码;1,如果之前存在文件,则覆盖之前的文件.如果没有,则创建新的文件.
//返回值:0,成功;其他,错误码.
u8 bmp_encode(u8 *filename,u16 x,u16 y,u16 width,u16 height,u8 mode)
{
FIL* f_bmp;
u16 bmpheadsize; //bmp头大小
BITMAPINFO hbmp; //bmp头
u8 res=0;
u16 tx,ty; //图像尺寸
u16 *databuf; //数据缓存区地址
u16 pixcnt; //像素计数器
u16 bi4width; //水平像素字节数
if(width==0||height==0)return PIC_WINDOW_ERR; //区域错误
if((x+width-1)>lcddev.width)return PIC_WINDOW_ERR; //区域错误
if((y+height-1)>lcddev.height)return PIC_WINDOW_ERR; //区域错误
#if BMP_USE_MALLOC == 1 //使用malloc
databuf=(u16*)mymalloc(1024); //开辟至少bi4width大小的字节的内存区域 ,对240宽的屏,480个字节就够了.
if(databuf==NULL)return PIC_MEM_ERR; //内存申请失败.
f_bmp=(FIL *)mymalloc(sizeof(FIL)); //开辟FIL字节的内存区域
if(f_bmp==NULL) //内存申请失败.
{
myfree(databuf);
return PIC_MEM_ERR;
}
#else
databuf=(u16*)bmpreadbuf;
f_bmp=&f_bfile;
#endif
bmpheadsize=sizeof(hbmp);//得到bmp文件头的大小
mymemset((u8*)&hbmp,0,sizeof(hbmp));//置零空申请到的内存.
hbmp.bmiHeader.biSize=sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER);//信息头大小
hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth=width; //bmp的宽度
hbmp.bmiHeader.biHeight=height; //bmp的高度
hbmp.bmiHeader.biPlanes=1; //恒为1
hbmp.bmiHeader.biBitCount=16; //bmp为16位色bmp
hbmp.bmiHeader.biCompression=BI_BITFIELDS;//每个象素的比特由指定的掩码决定。
hbmp.bmiHeader.biSizeImage=hbmp.bmiHeader.biHeight*hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth*hbmp.bmiHeader.biBitCount/8;//bmp数据区大小
hbmp.bmfHeader.bfType=((u16)'M'<<8)+'B';//BM格式标志
hbmp.bmfHeader.bfSize=bmpheadsize+hbmp.bmiHeader.biSizeImage;//整个bmp的大小
hbmp.bmfHeader.bfOffBits=bmpheadsize;//到数据区的偏移
hbmp.RGB_MASK[0]=0X00F800; //红色掩码
hbmp.RGB_MASK[1]=0X0007E0; //绿色掩码
hbmp.RGB_MASK[2]=0X00001F; //蓝色掩码
if(mode==1)res=f_open(f_bmp,(const TCHAR*)filename,FA_READ|FA_WRITE);//尝试打开之前的文件
if(mode==0||res==0x04)res=f_open(f_bmp,(const TCHAR*)filename,FA_WRITE|FA_CREATE_NEW);//模式0,或者尝试打开失败,则创建新文件
if((hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth*2)%4)//水平像素(字节)不为4的倍数
{
bi4width=((hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth*2)/4+1)*4;//实际要写入的宽度像素,必须为4的倍数.
}else bi4width=hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth*2; //刚好为4的倍数
if(res==FR_OK)//创建成功
{
res=f_write(f_bmp,(u8*)&hbmp,bmpheadsize,&bw);//写入BMP首部
for(ty=y+height-1;hbmp.bmiHeader.biHeight;ty--)
{
pixcnt=0;
for(tx=x;pixcnt!=(bi4width/2);)
{
if(pixcnt<hbmp.bmiHeader.biWidth)databuf[pixcnt]=LCD_ReadPoint(tx,ty);//读取坐标点的值
else databuf[pixcnt]=0Xffff;//补充白色的像素.
pixcnt++;
tx++;
}
hbmp.bmiHeader.biHeight--;
res=f_write(f_bmp,(u8*)databuf,bi4width,&bw);//写入数据
}
f_close(f_bmp);
}
#if BMP_USE_MALLOC == 1 //使用malloc
myfree(databuf);
myfree(f_bmp);
#endif
return res;
}
- 随机文章
- 热门文章
- 热评文章
- UDP打洞原理及代码
- C# 非独占延时函数 非Sleep
- C#图片处理示例(裁剪,缩放,清晰度,水印)
- 物联网 WIFI 一键配置原理(smartconfig) ESP8266/QCA4004
- 单片机时钟周期,机器周期,指令周期的区别
- C#全局监听Windows键盘事件
- FAT、NTFS、ExFAT文件系统详解
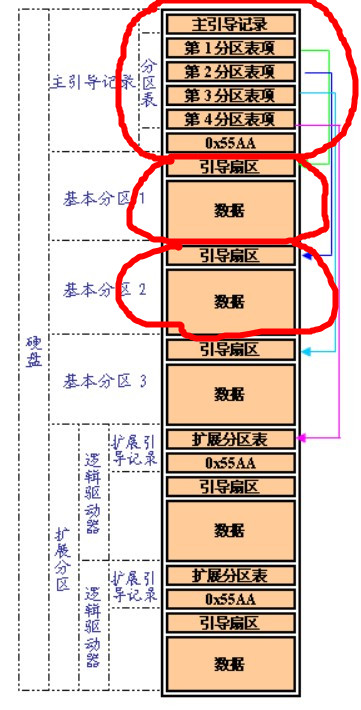
- 硬盘分区表、硬盘存储文件详解